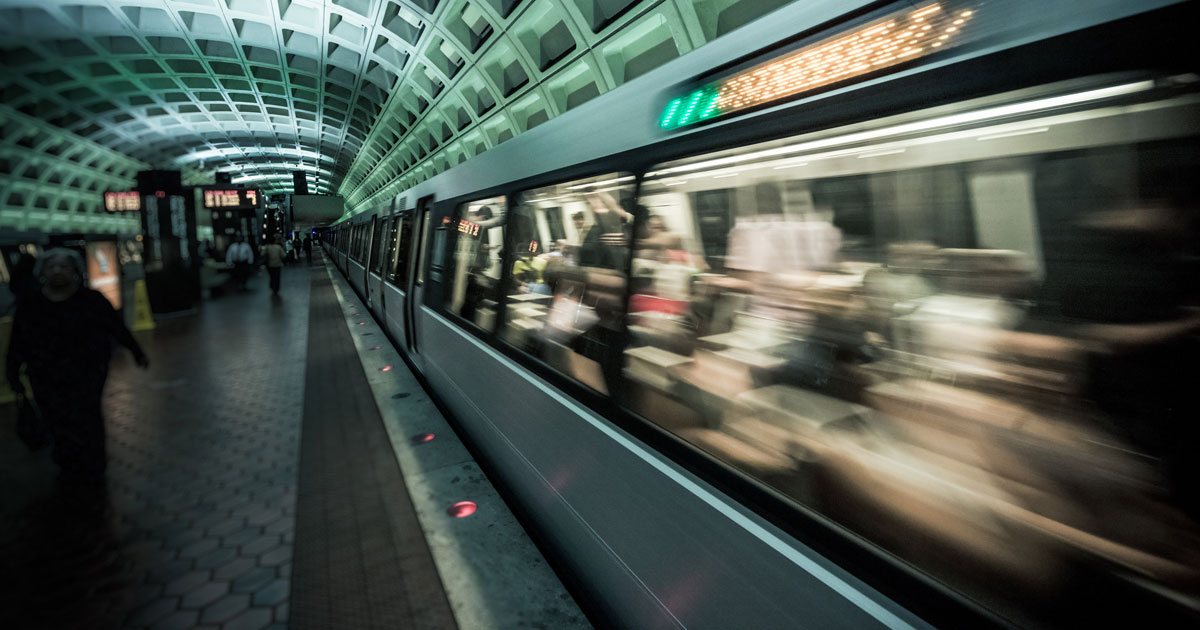
Rail transportation systems are a great example of a longstanding industry that is always looking for new ways to become more efficient, safer, and more effective at moving passengers and goods across rails.
From the New York City subway to transcontinental rail on every continent but Antarctica, rail lines are essential arteries of the global economy.
In this article, we take a look at some important recent trends.
Rail Trend One: Intermodal Freight Rail Continues to Expand
“In 2019, U.S. rail intermodal volume was 13.7 million units and intermodal accounted for approximately 25% of revenue for major U.S. railroads, more than any other single commodity group and well ahead of coal, which in the past was usually the largest single source of rail revenue.” - Association of American Railroads
Intermodal transportation refers to shipping using containers or truck trailers which are designed to be readily transferable between maritime, rail, and automotive shipping methods.
The container is increasingly dominating intermodal transport, and railroads are no exception. Since its inception in the 1950s, the rise of the “container,” which is standardized for maritime shipping and land-based transportation, is one of the most dominant trends in logistics. They continue to count for an ever-increasing share of overall freight. According to the Association of American Railroads, containers accounted for:
- 47% of intermodal volume in 1990.
- 69% in 2000.
- 92% in 2019.
Containers can be double-stacked on ships and trains, allowing for much greater efficiency compared to traditional truck trailers. Modern port infrastructure also allows for the rapid transfer of containers between ships and trucks/trains using specialized cranes.
These containers are a great example of improved transportation integration offering more efficient options for shipping customers. Efficient intermodal containers allow customers to benefit from the geographic flexibility of trucks without sacrificing the superior per-mile costs of rail. The intermodal approach first became prominent in import/export shipping but has become increasingly common in domestic shipping.
Rail Trend Two: A Focus on Digitalization and Cyber-Security
Digital innovation is everywhere in today’s economy, and rail transportation is no exception. With sprawling physical infrastructure, rail networks provide a prime opportunity for improved integration of sensors with physical infrastructure (the much-hyped “internet of things”).
Cisco estimates that $30 billion will be spent on IoT projects for rail over the next 12 years. Myriad potential applications include more detailed passenger tracking and feedback, preventative maintenance sensors to reduce long term TCO, and real-time incident alarms. Meanwhile, automated trains are slowly expanding in scope.
Finally, cybersecurity is an increasing concern that comes alongside greater reliance on digital tools. As crucial infrastructure, rail networks represent a potentially attractive target for cyber attacks. This article in Railway Review provides an excellent interview of the rail cybersecurity landscape.
Rail Trend Three: Chemicals as Prime Freight
“The American Chemistry Council estimates that an additional 300,000 annual rail shipments will be required to meet increased production by 2023. From our analysis, that translates to about 40% of their projected volume growth moving via rail.” - AAR
Coal was traditionally the number one commodity shipped by rail. While the decline of coal continues to reduce rail traffic for this commodity, chemical shipping is emerging as a promising alternative growth market.
Rail offers a safe, cost-effective method for shipping chemicals, which now command the second-largest share of revenue of any freight (more than coal and behind only intermodal freight). The chemicals category includes everything from plastics to pharmaceuticals, consumer goods to toxic compounds.
Continued investment in safe rail car operation conditions has helped mitigate the risks associated with shipping hazardous or highly flammable materials. TriStar has some ground-level experience with this trend: we have been using our flame retardant composites to help rail OEM’s achieve better fire safety alongside improved performance (learn more here).
Rail Trend Four: The Resurgence of Passenger Rail?
“Rail is among the most energy-efficient modes of transport for freight and passengers - while the rail sector carries 8% of the world’s passengers and 7% of global freight transport, it represents only 2% of total transport energy demand.” - IEA
Passenger rail experienced a long decline as new transportation methods like air and the interstate highway system proliferated. Amtrak long exhibited widely criticized financial performance, but things may be beginning to turn around.
Growing congestion at airports and on highways, coupled with an increasingly carbon-conscious consumer population, are driving renewed demand for train travel.
For now, passenger lines are focused on major inter-urban corridors, like San Diego-Los Angeles and Milwaukee-Chicago. The Northeast Corridor from NYC to Boston remains Amtrak’s best growth driver. Long-distance routes, however, continue to operate at a loss.
New technologies are opening up new options for passenger travel. In Europe, for instance, high-speed trains are offering increasingly competitive travel times between highly trafficked routes like Paris-London. High-speed trains, however, require substantial infrastructure investments that were public-led in Europe but remain elusive for a US passenger system which has seen substantially less government investment.
Forbes provides a good summary of the current state of play for passenger rail here. For a deeper look at train energy efficiency and how this could lead to a rail resurgence, we recommend this article by the International Energy Agency.
Learning More
- For a broader overview of the rail industry and rail growth trends, please see our Rail Industry overview blog post. In this article, we take a look at some of the most important types of rail equipment.
TriStar works closely with a number of rail manufacturers to select advanced material components that solve key industry challenges (like the need for flame-retardant components). We bring our engineering-driven approach to bear on every client project, ensuring the right materials are selected.
To read more about why bearings and similar components are so important for rail car technology, please see the article linked below.
If you’d like to reach out to learn more about using TriStar’s self-lubricating composites to solve rail engineering pain points, just click the button below.