Rugged Rulon 1337 for slide pads and rolling element retainers
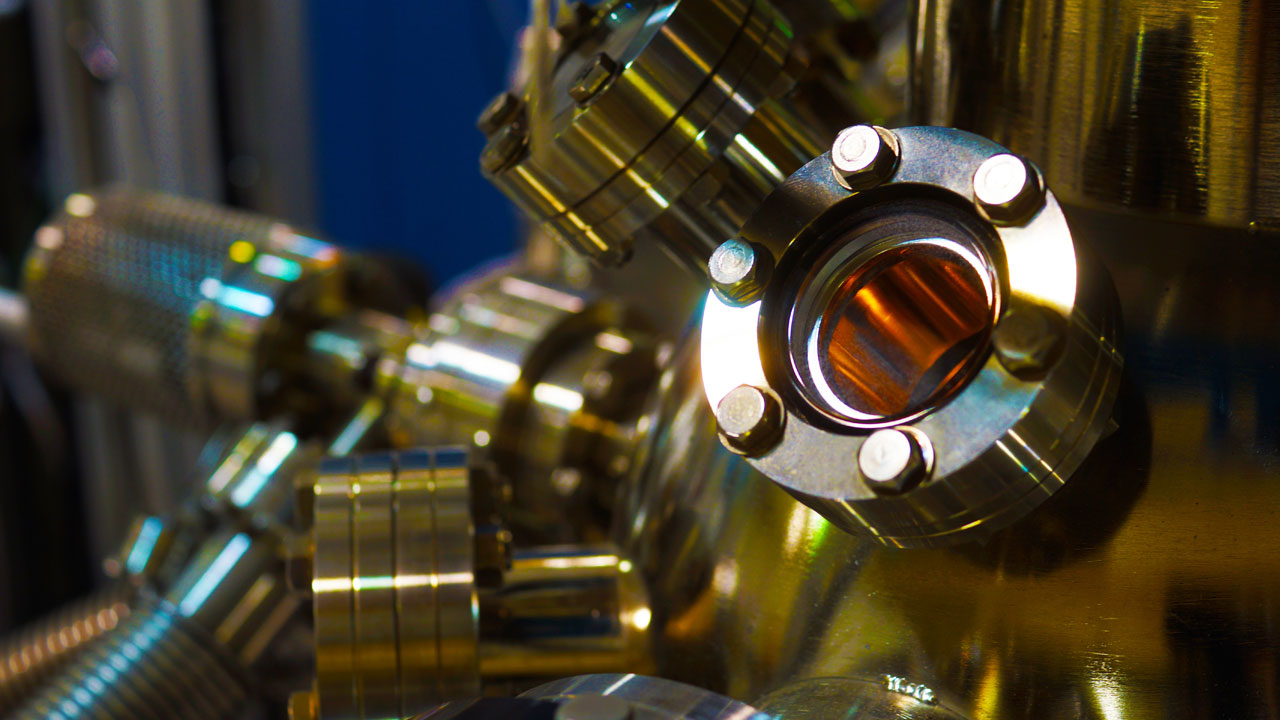
When a major manufacturer of vacuum chambers needed to replace failing metal bearings in a critical low-pressure environment, the Tristar Engineering team was called in to help. After a detailed site evaluation, our experts recommended Rulon® 1337, a high-performance self-lubricating bearing material engineered for vacuum and cleanroom applications.
Rulon 1337 is composed entirely of FDA-compliant materials and is known for its exceptional durability, low friction, and chemical resistance. These characteristics make it ideal for industries like food processing, semiconductor manufacturing, aerospace testing, and precision instrumentation, where traditional lubricants can’t be used.
Vacuum Chamber Challenges and the Need for Self-Lubricating Bearings
Vacuum chamber systems operate by removing air and gases through high-efficiency pumps, creating an environment where metal bearings often fail due to lack of lubrication and thermal stress. In these conditions, grease and oil can outgas or evaporate, leading to contamination, friction buildup, and mechanical wear.
Rulon 1337 bearings, however, are engineered to thrive in vacuum environments. Their self-lubricating structure ensures consistent performance without external lubricants, even under low-pressure and high-temperature conditions.
These rugged polymer bearings deliver superior performance in two primary vacuum chamber components:
1. Slide Pads That Provide Superior Support and Stability
Traditional stainless steel or bronze bearings are often assumed to be the strongest options for linear slide systems. However, Rulon 1337 bearings provide equal structural strength with far greater operational efficiency.
Rulon’s low coefficient of friction and high compressive strength make it ideal for X, Y, and Z linear slides used in vacuum chamber positioning systems.
Since switching to Rulon 1337 slide pads, our client has reported:
- Longer service life between maintenance cycles
- Reduced friction across precision sliding interfaces
- No need for re-lubrication, even in low-pressure environments
These improvements have directly enhanced uptime and reduced overall operational costs.
Expert Note from Tristar: In vacuum systems, lubrication failure and material outgassing are the most common causes of component degradation. Rulon 1337 eliminates both issues with a solid lubricant matrix that maintains surface film integrity under vacuum. Tristar’s material testing confirms stable friction coefficients and zero outgassing contamination, making Rulon ideal for precision vacuum chambers, optical instruments, and aerospace systems.
2. Rolling Element Retainers with Self-Lubricating Precision
In addition to slide pads, the client required a maintenance-free replacement for the rolling element retainers used in chamber motion systems.
Rulon 1337 proved to be the perfect fit. Its self-lubricating design allows for smooth, silent movement of rolling elements without grease, while its dimensional stability prevents deformation under continuous vacuum exposure.
Key performance benefits include:
- High load-bearing capacity under vacuum compression
- Excellent friction and thermal properties
- Compatibility with various mating surfaces, including stainless steel and aluminum
- Resistance to deformation from pressure differentials
Since installation, the Rulon retainers have performed flawlessly, extending the lifespan of the rolling elements and eliminating the need for manual lubrication.
Expert Note from Tristar: Metal retainers tend to deform over time in high-vacuum or thermal cycling environments. Rulon 1337’s reinforced polymer structure maintains its geometry, even under mechanical stress and extreme temperature variation. For vacuum or cleanroom applications where contamination control is critical, Rulon composites outperform both metals and PTFE alone.
Additional Resources
If you’re considering Rulon 1337 for your application, explore the following resources:
- Read our specification sheet for Rulon 1337.
- Rulon Materials Comparison Chart: Compare grades for thermal, mechanical, and chemical resistance.
- Rulon Technical White Papers: Learn about the different Rulon grades and read application case studies across aerospace, industrial automation, and medical devices.